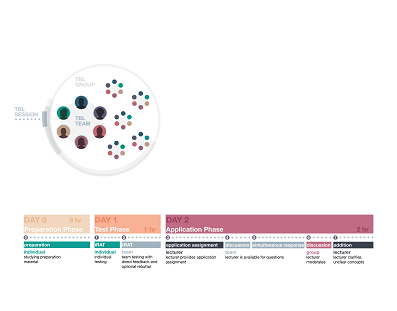
TBL is an active teaching method, also using the flipped classroom method. In TBL, students individually prepare theory or a question before each class and take a test on this subject individually, the individual Readiness Assurance Test (iRAT). Afterwards, they answer the same questions together in small teams of six students (tRAT). The correct answers are discussed in class with all groups after the test.
This is followed by the elaboration or application phase, in which the team further deepens and applies the knowledge they have acquired. For instance, by answering multiple choice or open questions, follow-up questions and solving even more complex problems. However, the solution is often not straightforward and can only be solved collaboratively The goal is to be able to substantiate the answer as a team. This phase includes discussion, role playing, and analysis. The teams themselves are responsible for carrying out the tasks, dividing the tasks and ensuring that all members of the team are involved.
TBL teams remain together throughout the academic year so that each student takes on the role of chairman or spokesperson at least once, for example. The teacher functions as a coach for the learning process in these phases.
TBL is applied at ACTA in the Bachelor of Dental Medicine and the Faculty of Social Sciences.
Why TBL?
The underlying idea of TBL is that cooperation and social interaction stimulates learning. Students are interdependent and therefore feel more motivated and responsible for active participation. The emphasis in TBL is less on memorising knowledge and more on application, analysis, cooperation, and communication. Later in their professional lives, students will also often work together, so the earlier they develop these skills, the better.
TBL also connects the five principles of effective learning according to Merrill's (2012) theory, the students:
- learn from real life problems and carry out professional tasks in small groups;
- activate their previous knowledge;
- apply new knowledge immediately;
- integrate the new knowledge and transfer it;
- present their new knowledge and understanding to fellow students.
TBL thus provides a more profound understanding of new knowledge, a higher level in Bloom's taxonomy. This way the levels of applying, analysing, evaluating and creating are also reached, on top of remembering and understanding.